Child-Pugh-Turcotte (CPT) 分数[8]Child CG, Turcotte JG. Surgery and portal hypertension. Major Probl Clin Surg. 1964;1:1-85.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/4950264?tool=bestpractice.com[9]Pugh RN, Murray-Lyon IM, Dawson JL, et al. Transection of the oesophagus for bleeding oesophageal varices. Br J Surg. 1973;60:646-649.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/4541913?tool=bestpractice.com
CPT分数是衡量肝硬化严重程度最常采用的评分系统之一。[8]Child CG, Turcotte JG. Surgery and portal hypertension. Major Probl Clin Surg. 1964;1:1-85.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/4950264?tool=bestpractice.com[9]Pugh RN, Murray-Lyon IM, Dawson JL, et al. Transection of the oesophagus for bleeding oesophageal varices. Br J Surg. 1973;60:646-649.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/4541913?tool=bestpractice.comCPT基于腹水、肝性脑病、血清胆红素、白蛋白和凝血分析(PT和INR),分为Child A、B、C三个等级,提示病情逐渐加重。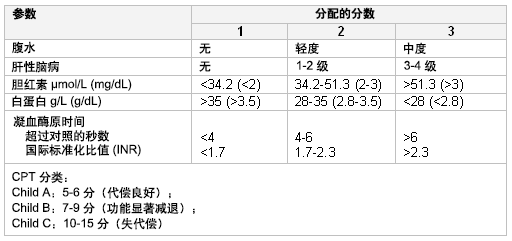 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Child-Pugh-Turcotte评分系统由 Dr Keith Lindor 提供;经获准使用 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Child-Pugh-Turcotte评分系统由 Dr Keith Lindor 提供;经获准使用 [Citation ends].
终末期肝病模型 (Model of End-Stage Liver Disease, MELD)[12]Kamath PS, Wiesner RH, Malinchoc M, et al. A model to predict survival in patients with end-stage liver disease. Hepatology. 2001;33:464-470.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11172350?tool=bestpractice.com
MELD 评分是一个最近用于衡量肝硬化严重程度的评分系统,根据血清胆红素、钠、肌酐、凝血分析 (INR和凝血酶原时间) 通过特定的计算机程序计算得到。Model of End-Stage Liver Disease (MELD)[11]Kim WR, Biggins SW, Kremers WK, et al. Hyponatremia and mortality among patients on the liver-transplant waiting list. N Engl J Med. 2008;359:1018-1026.http://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMoa0801209#t=articlehttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18768945?tool=bestpractice.com[12]Kamath PS, Wiesner RH, Malinchoc M, et al. A model to predict survival in patients with end-stage liver disease. Hepatology. 2001;33:464-470.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11172350?tool=bestpractice.com在美国,MELD是移植肝分配依据的分类系统。
 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Child-Pugh-Turcotte评分系统由 Dr Keith Lindor 提供;经获准使用 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Child-Pugh-Turcotte评分系统由 Dr Keith Lindor 提供;经获准使用 [Citation ends].