单纯依靠病史和体格检查通常不足以确认或排除疾病。由于其在发病 2 小时内的死亡风险最高,所以对此疾病应高度警惕并进行迅速有效的管理。[73]Bĕlohlávek J, Dytrych V, Linhart A. Pulmonary embolism, part I: Epidemiology, risk factors and risk stratification, pathophysiology, clinical presentation, diagnosis and nonthrombotic pulmonary embolism. Exp Clin Cardiol. 2013 Spring;18(2):129-38.https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3718593/http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23940438?tool=bestpractice.com 一项研究显示,最后死于肺栓塞的患者中有70% 未曾怀疑诊断患有 PE。[6]Stein PD, Henry JW. Prevalence of acute pulmonary embolism among patients in a general hospital and at autopsy. Chest. 1995 Oct;108(4):978-81.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/7555172?tool=bestpractice.com 在死亡患者中,有 79% 的患者在发病后 1 小时内死亡, 93% 的患者在 2.5 小时内死亡。[6]Stein PD, Henry JW. Prevalence of acute pulmonary embolism among patients in a general hospital and at autopsy. Chest. 1995 Oct;108(4):978-81.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/7555172?tool=bestpractice.com
由已经验证的预测规则和/或临床判断来评估肺栓塞的临床概率,是所有肺栓塞诊断策略的基础。[74]Raja AS, Greenberg JO, Qaseem A, et al. Evaluation of patients with suspected acute pulmonary embolism: best practice advice from the Clinical Guidelines Committee of the American College of Physicians. Ann Intern Med. 2015 Nov 3;163(9):701-11.http://annals.org/aim/fullarticle/2443959/evaluation-patients-suspected-acute-pulmonary-embolism-best-practice-advice-fromhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26414967?tool=bestpractice.com[75]Konstantinides SV, Torbicki A, Agnelli G, et al; Task Force for the Diagnosis and Management of Acute Pulmonary Embolism of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). 2014 ESC guidelines on the diagnosis and management of acute pulmonary embolism. Eur Heart J. 2014 Nov 14;35(43):3033-69.https://academic.oup.com/eurheartj/article/35/43/3033/503581http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25173341?tool=bestpractice.com对于有中度 PE 临床可能性的血流动力学稳定患者,推荐进行 D-二聚体检测以评估影像学检查的需要。[74]Raja AS, Greenberg JO, Qaseem A, et al. Evaluation of patients with suspected acute pulmonary embolism: best practice advice from the Clinical Guidelines Committee of the American College of Physicians. Ann Intern Med. 2015 Nov 3;163(9):701-11.http://annals.org/aim/fullarticle/2443959/evaluation-patients-suspected-acute-pulmonary-embolism-best-practice-advice-fromhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26414967?tool=bestpractice.com对于 PE 临床可能性极低的患者,D-二聚体检测用于那些未满足所有肺栓塞排除标准 (PERC) 的患者。[74]Raja AS, Greenberg JO, Qaseem A, et al. Evaluation of patients with suspected acute pulmonary embolism: best practice advice from the Clinical Guidelines Committee of the American College of Physicians. Ann Intern Med. 2015 Nov 3;163(9):701-11.http://annals.org/aim/fullarticle/2443959/evaluation-patients-suspected-acute-pulmonary-embolism-best-practice-advice-fromhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26414967?tool=bestpractice.com对于有高度 PE 临床可能性的患者应立即进行 CT 肺动脉造影(或者若禁忌进行 CT 肺动脉造影,则可行肺通气-灌注 [V/Q] 扫描),任何伴有休克或低血压的疑似 PE 患者也应立即进行此检查。由于 PE 的治疗有显著的出血风险,故使用确定性检查确诊 PE 至关重要。
病史
病史通常提示有急性发作的症状。然而,一个多中心急诊 PE 登记处显示,PE 可能没有任何症状(而在其他疾病的诊断检查过程中或在尸检中被意外发现),或具有非特异性的症状和体征。[76]Pollack CV, Schreiber D, Goldhaber SZ, et al. Clinical characteristics, management, and outcomes of patients diagnosed with acute pulmonary embolism in the emergency department: initial report of EMPEROR (Multicenter Emergency Medicine Pulmonary Embolism in the Real World Registry). J Am Coll Cardiol. 2011 Feb 8;57(6):700-6.http://www.onlinejacc.org/content/57/6/700http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21292129?tool=bestpractice.com
胸膜炎性胸痛和呼吸困难是最常见的症状。[76]Pollack CV, Schreiber D, Goldhaber SZ, et al. Clinical characteristics, management, and outcomes of patients diagnosed with acute pulmonary embolism in the emergency department: initial report of EMPEROR (Multicenter Emergency Medicine Pulmonary Embolism in the Real World Registry). J Am Coll Cardiol. 2011 Feb 8;57(6):700-6.http://www.onlinejacc.org/content/57/6/700http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21292129?tool=bestpractice.com[77]Bajaj N, Bozarth AL, Guillot J, et al. Clinical features in patients with pulmonary embolism at a community hospital: analysis of 4 years of data. J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2014 Apr;37(3):287-92.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23681675?tool=bestpractice.com患者常自诉恐惧感。[3]Bell WR, Simon TL, DeMets DL. The clinical features of submassive and massive pulmonary emboli. Am J Med. 1977 Mar;62(3):355-60.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/842555?tool=bestpractice.com[78]Stein PD, Willis PW 3rd, DeMets DL. History and physical examination in acute pulmonary embolism in patients without preexisting cardiac or pulmonary disease. Am J Cardiol. 1981 Feb;47(2):218-23.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/7468469?tool=bestpractice.com较少出现咯血和晕厥,后者提示血栓负荷更重及预后更差。[75]Konstantinides SV, Torbicki A, Agnelli G, et al; Task Force for the Diagnosis and Management of Acute Pulmonary Embolism of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). 2014 ESC guidelines on the diagnosis and management of acute pulmonary embolism. Eur Heart J. 2014 Nov 14;35(43):3033-69.https://academic.oup.com/eurheartj/article/35/43/3033/503581http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25173341?tool=bestpractice.com[76]Pollack CV, Schreiber D, Goldhaber SZ, et al. Clinical characteristics, management, and outcomes of patients diagnosed with acute pulmonary embolism in the emergency department: initial report of EMPEROR (Multicenter Emergency Medicine Pulmonary Embolism in the Real World Registry). J Am Coll Cardiol. 2011 Feb 8;57(6):700-6.http://www.onlinejacc.org/content/57/6/700http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21292129?tool=bestpractice.com[77]Bajaj N, Bozarth AL, Guillot J, et al. Clinical features in patients with pulmonary embolism at a community hospital: analysis of 4 years of data. J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2014 Apr;37(3):287-92.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23681675?tool=bestpractice.com
应明确深静脉血栓形成 (DVT) 或 PE 的危险因素。如果患者有 DVT 或 PE 家族史或复发性流产病史,提示可能存在遗传性易栓症。[18]Horlander KT, Mannino DM, Leeper KV. Pulmonary embolism mortality in the United States, 1979-1998: an analysis using multiple-cause mortality data. Arch Intern Med. 2003 Jul 28;163(14):1711-7.https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamainternalmedicine/fullarticle/215882http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12885687?tool=bestpractice.com[30]Martínez-Zamora MÁ, Cervera R, Balasch J. Thromboembolism risk following recurrent miscarriage. Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther. 2013 Nov;11(11):1503-13.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24134441?tool=bestpractice.com[36]Bates SM, Greer IA, Middeldorp S, et al. VTE, thrombophilia, antithrombotic therapy, and pregnancy. Antithrombotic therapy and prevention of thrombosis, 9th ed: American College of Chest Physicians evidence-based clinical practice guidelines. Chest. 2012 Feb;141(2 Suppl):e691S-736S.https://journal.chestnet.org/article/S0012-3692(12)60136-6/fulltexthttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22315276?tool=bestpractice.com[57]Croles FN, Nasserinejad K, Duvekot JJ, et al. Pregnancy, thrombophilia, and the risk of a first venous thrombosis: systematic review and bayesian meta-analysis. BMJ. 2017 Oct 26;359:j4452.https://www.bmj.com/content/359/bmj.j4452.longhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29074563?tool=bestpractice.com 遗传性和获得性(例如,抗磷脂综合征)易栓症可导致复发性流产。其他 DVT 或 PE 的严重危险因素包括:年龄增长;发生 DVT;近 2 个月内有手术史;有>5 日的卧床休息史;既往静脉血栓栓塞事件病史;活动性恶性病变;近期外伤或骨折史;妊娠/产后期;下肢瘫痪;凝血因子 V Leiden 或凝血酶原基因突变;抗凝血酶、蛋白 C 或蛋白 S 缺乏。[19]Goldhaber SZ, Visani L, De Rosa M. Acute pulmonary embolism: clinical outcomes in the International Cooperative Pulmonary Embolism Registry (ICOPER). Lancet. 1999 Apr 24;353(9162):1386-9.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10227218?tool=bestpractice.com[57]Croles FN, Nasserinejad K, Duvekot JJ, et al. Pregnancy, thrombophilia, and the risk of a first venous thrombosis: systematic review and bayesian meta-analysis. BMJ. 2017 Oct 26;359:j4452.https://www.bmj.com/content/359/bmj.j4452.longhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29074563?tool=bestpractice.com
体格检查
体格检查通常为非特异性。[76]Pollack CV, Schreiber D, Goldhaber SZ, et al. Clinical characteristics, management, and outcomes of patients diagnosed with acute pulmonary embolism in the emergency department: initial report of EMPEROR (Multicenter Emergency Medicine Pulmonary Embolism in the Real World Registry). J Am Coll Cardiol. 2011 Feb 8;57(6):700-6.http://www.onlinejacc.org/content/57/6/700http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21292129?tool=bestpractice.com 尽管如此,当患者出现有疑似 PE 的临床表现时,应立即对其行进一步的客观检查以确定诊断。
对于大多数患者,如果其表现有呼吸困难、胸痛、先兆晕厥或晕厥和/或咯血症状时,应怀疑患 PE 的可能。[76]Pollack CV, Schreiber D, Goldhaber SZ, et al. Clinical characteristics, management, and outcomes of patients diagnosed with acute pulmonary embolism in the emergency department: initial report of EMPEROR (Multicenter Emergency Medicine Pulmonary Embolism in the Real World Registry). J Am Coll Cardiol. 2011 Feb 8;57(6):700-6.http://www.onlinejacc.org/content/57/6/700http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21292129?tool=bestpractice.com[79]Miniati M, Prediletto R, Formichi B, et al. Accuracy of clinical assessment in the diagnosis of pulmonary embolism. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1999 Mar;159(3):864-71.https://www.atsjournals.org/doi/full/10.1164/ajrccm.159.3.9806130http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10051264?tool=bestpractice.com[80]Wells PS, Ginsberg JS, Anderson DR, et al. Use of a clinical model for safe management of patients with suspected pulmonary embolism. Ann Intern Med. 1998 Dec 15;129(12):997-1005.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9867786?tool=bestpractice.com 胸痛是较为常见的症状,且通常是由远端栓子所导致的肺梗死而形成的胸膜刺激引起的。[81]Stein PD, Henry JW. Clinical characteristics of patients with acute pulmonary embolism stratified according to their presenting syndromes. Chest. 1997 Oct;112(4):974-9.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9377961?tool=bestpractice.com 在中央型 PE(血栓出现于肺动脉干、左或右肺动脉),可出现有类心绞痛样的胸痛,其可能由右心室缺血导致。如果出现此类临床表现,需要与急性冠脉综合征或主动脉夹层进行鉴别。晕厥症状较少见,但不论是否存在血流动力学不稳定,均可出现。[76]Pollack CV, Schreiber D, Goldhaber SZ, et al. Clinical characteristics, management, and outcomes of patients diagnosed with acute pulmonary embolism in the emergency department: initial report of EMPEROR (Multicenter Emergency Medicine Pulmonary Embolism in the Real World Registry). J Am Coll Cardiol. 2011 Feb 8;57(6):700-6.http://www.onlinejacc.org/content/57/6/700http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21292129?tool=bestpractice.com[77]Bajaj N, Bozarth AL, Guillot J, et al. Clinical features in patients with pulmonary embolism at a community hospital: analysis of 4 years of data. J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2014 Apr;37(3):287-92.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23681675?tool=bestpractice.com[81]Stein PD, Henry JW. Clinical characteristics of patients with acute pulmonary embolism stratified according to their presenting syndromes. Chest. 1997 Oct;112(4):974-9.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9377961?tool=bestpractice.com 如果患者有 DVT 出现,可出现其他体征包括发热、咳嗽或单侧小腿肿胀/压痛。[76]Pollack CV, Schreiber D, Goldhaber SZ, et al. Clinical characteristics, management, and outcomes of patients diagnosed with acute pulmonary embolism in the emergency department: initial report of EMPEROR (Multicenter Emergency Medicine Pulmonary Embolism in the Real World Registry). J Am Coll Cardiol. 2011 Feb 8;57(6):700-6.http://www.onlinejacc.org/content/57/6/700http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21292129?tool=bestpractice.com[77]Bajaj N, Bozarth AL, Guillot J, et al. Clinical features in patients with pulmonary embolism at a community hospital: analysis of 4 years of data. J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2014 Apr;37(3):287-92.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23681675?tool=bestpractice.com
伴有休克或低血压的疑似 PE 患者
休克或低血压(收缩压 <90 mmHg)较少见;超过 95% 的急性 PE 患者血流动力学稳定。[82]Laporte S, Mismetti P, Décousus H, et al; RIETE Investigators. Clinical predictors for fatal pulmonary embolism in 15,520 patients with venous thromboembolism: findings from the Registro Informatizado de la Enfermedad TromboEmbolica venosa (RIETE) Registry. Circulation. 2008 Apr 1;117(13):1711-6.http://circ.ahajournals.org/content/117/13/1711.longhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18347212?tool=bestpractice.com然而,休克或低血压提示中央型 PE 和/或血流动力学储备严重减少。若 PE 已引起肺源性心脏病,患者可出现颈静脉压升高、胸骨隆起或肺动脉瓣区第 2 心音增强,不过这一情况罕见。[83]Bajaj R, Ramanakumar A, Mamidala S, et al. Successful treatment of mobile right atrial thrombus and acute pulmonary embolism with intravenous tissue plasminogen activator. BMJ Case Rep. 2013 Jul 25;2013:bcr2013010255.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23892824?tool=bestpractice.com[84]Matthews JC, McLaughlin V. Acute right ventricular failure in the setting of acute pulmonary embolism or chronic pulmonary hypertension: a detailed review of the pathophysiology, diagnosis, and management. Curr Cardiol Rev. 2008 Feb;4(1):49-59.https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2774585/http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19924277?tool=bestpractice.com
理想情况下,在开始溶栓治疗前,应通过CT 肺动脉造影 (CTPA) 确诊 PE。[75]Konstantinides SV, Torbicki A, Agnelli G, et al; Task Force for the Diagnosis and Management of Acute Pulmonary Embolism of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). 2014 ESC guidelines on the diagnosis and management of acute pulmonary embolism. Eur Heart J. 2014 Nov 14;35(43):3033-69.https://academic.oup.com/eurheartj/article/35/43/3033/503581http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25173341?tool=bestpractice.com[85]Konstantinides SV, Barco S, Lankeit M, et al. Management of pulmonary embolism: an update. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2016 Mar 1;67(8):976-90.http://www.onlinejacc.org/content/67/8/976http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26916489?tool=bestpractice.com不过,肺通气-灌注 (V/Q) 扫描结果阴性可有效排除 PE,并且为一种无辐射和无需造影剂的操作。[75]Konstantinides SV, Torbicki A, Agnelli G, et al; Task Force for the Diagnosis and Management of Acute Pulmonary Embolism of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). 2014 ESC guidelines on the diagnosis and management of acute pulmonary embolism. Eur Heart J. 2014 Nov 14;35(43):3033-69.https://academic.oup.com/eurheartj/article/35/43/3033/503581http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25173341?tool=bestpractice.com但若患者有即将发生心搏骤停的风险,则可仅基于临床表现即开始治疗。[86]British Thoracic Society Standards of Care Committee Pulmonary Embolism Guideline Development Group. British Thoracic Society guidelines for the management of suspected acute pulmonary embolism. Thorax. 2003 Jun;58(6):470-83.http://thorax.bmj.com/content/58/6/470.longhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12775856?tool=bestpractice.com
不伴有休克和低血压的疑似 PE 患者
当无法通过病史和体格检查排除 PE 时,应通过已经验证的预测规则和/或临床判断来确定 PE 的验前概率。[74]Raja AS, Greenberg JO, Qaseem A, et al. Evaluation of patients with suspected acute pulmonary embolism: best practice advice from the Clinical Guidelines Committee of the American College of Physicians. Ann Intern Med. 2015 Nov 3;163(9):701-11.http://annals.org/aim/fullarticle/2443959/evaluation-patients-suspected-acute-pulmonary-embolism-best-practice-advice-fromhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26414967?tool=bestpractice.com[75]Konstantinides SV, Torbicki A, Agnelli G, et al; Task Force for the Diagnosis and Management of Acute Pulmonary Embolism of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). 2014 ESC guidelines on the diagnosis and management of acute pulmonary embolism. Eur Heart J. 2014 Nov 14;35(43):3033-69.https://academic.oup.com/eurheartj/article/35/43/3033/503581http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25173341?tool=bestpractice.com预测规则可能更为理想,尤其是对于很少评估 PE 的临床医生,因为临床判定缺乏标准化。[74]Raja AS, Greenberg JO, Qaseem A, et al. Evaluation of patients with suspected acute pulmonary embolism: best practice advice from the Clinical Guidelines Committee of the American College of Physicians. Ann Intern Med. 2015 Nov 3;163(9):701-11.http://annals.org/aim/fullarticle/2443959/evaluation-patients-suspected-acute-pulmonary-embolism-best-practice-advice-fromhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26414967?tool=bestpractice.com[75]Konstantinides SV, Torbicki A, Agnelli G, et al; Task Force for the Diagnosis and Management of Acute Pulmonary Embolism of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). 2014 ESC guidelines on the diagnosis and management of acute pulmonary embolism. Eur Heart J. 2014 Nov 14;35(43):3033-69.https://academic.oup.com/eurheartj/article/35/43/3033/503581http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25173341?tool=bestpractice.com[87]Lucassen W, Geersing GJ, Erkens PM, et al. Clinical decision rules for excluding pulmonary embolism: a meta-analysis. Ann Intern Med. 2011 Oct 4;155(7):448-60.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21969343?tool=bestpractice.com
评估临床患 PE 的可能性
通过使用原始 Wells 评分(修订)、简化 Wells 评分(修订)、原始 Geneva 评分(改良)或简化 Geneva 评分(改良),可将疑似 PE 患者依据临床(验前)概率分成不同的类别,该分类符合确诊 PE 的实际患病率。[75]Konstantinides SV, Torbicki A, Agnelli G, et al; Task Force for the Diagnosis and Management of Acute Pulmonary Embolism of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). 2014 ESC guidelines on the diagnosis and management of acute pulmonary embolism. Eur Heart J. 2014 Nov 14;35(43):3033-69.https://academic.oup.com/eurheartj/article/35/43/3033/503581http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25173341?tool=bestpractice.com[88]Wells PS, Anderson DR, Rodger M, et al. Derivation of a simple clinical model to categorize patients' probability of pulmonary embolism: increasing the model's utility with the SimpliRED D-dimer. Thromb Haemost. 2000 Mar;83(3):416-20.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10744147?tool=bestpractice.com[89]Le Gal G, Righini M, Roy PM, et al. Prediction of pulmonary embolism in the emergency department: the revised Geneva score. Ann Intern Med. 2006 Feb 7;144(3):165-71.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16461960?tool=bestpractice.com 这些临床决策工具为一系列的病史和体格检查特征赋值(一分或多分),分值总和决定是否有患 PE 的可能性。
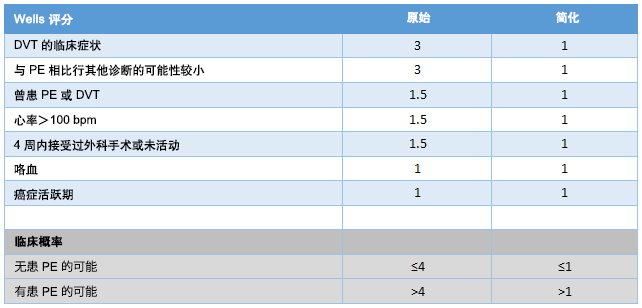 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 原始和简化 Wells 评分标准(修订)由 BMJ Knowledge Centre 编制 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 原始和简化 Wells 评分标准(修订)由 BMJ Knowledge Centre 编制 [Citation ends].
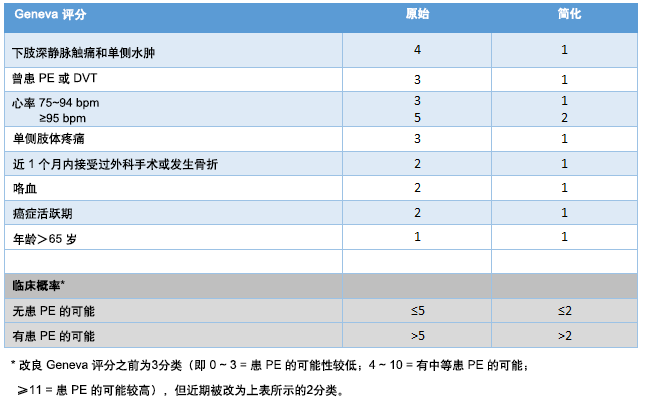 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 原始和简化 Geneva 评分标准(改良)由 BMJ Knowledge Centre 编制 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 原始和简化 Geneva 评分标准(改良)由 BMJ Knowledge Centre 编制 [Citation ends].
由于使用简便,简化版的修订 Wells 评分标准和改良 Geneva 评分标准在临床上可能是首选。[90]van Es N, Kraaijpoel N, Klok FA, et al. The original and simplified Wells rules and age-adjusted D-dimer testing to rule out pulmonary embolism: an individual patient data meta-analysis. J Thromb Haemost. 2017 Apr;15(4):678-84.https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/jth.13630http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28106338?tool=bestpractice.com两种简化版的评分标准都已经验证;未证明两者中的其中一种优于另一种。[74]Raja AS, Greenberg JO, Qaseem A, et al. Evaluation of patients with suspected acute pulmonary embolism: best practice advice from the Clinical Guidelines Committee of the American College of Physicians. Ann Intern Med. 2015 Nov 3;163(9):701-11.http://annals.org/aim/fullarticle/2443959/evaluation-patients-suspected-acute-pulmonary-embolism-best-practice-advice-fromhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26414967?tool=bestpractice.com[91]Hendriksen JM, Geersing GJ, Lucassen WA, et al. Diagnostic prediction models for suspected pulmonary embolism: systematic review and independent external validation in primary care. BMJ. 2015 Sep 8;351:h4438.https://www.bmj.com/content/351/bmj.h4438.longhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26349907?tool=bestpractice.com但是,Geneva 评分完全基于客观的临床指标,故可能重复性更强(Wells 评分标准 [原始和简化版] 包括主观的‘其他鉴别诊断的可能性低于 PE’这一临床指标)。[92]Klok FA, Kruisman E, Spaan J, et al. Comparison of the revised Geneva score with the Wells rule for assessing clinical probability of pulmonary embolism. J Thromb Haemost. 2008 Jan;6(1):40-4.https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/j.1538-7836.2007.02820.xhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17973649?tool=bestpractice.com
Wells 评分标准和修订的 Geneva 评分标准将患者分为两类(不太可能发生 PE 和很有可能发生 PE)。但是,每个工具的早期迭代将 PE 的临床可能性归为低、中或高度。若使用两级分类法,在很有可能发生 PE 的这类患者中,有 50% 最终确诊 PE,而不太可能发生 PE 的这类患者中有 12% 最终确诊。若使用三级分类法,确诊 PE 的患者比例在低可能性分类患者中为 10%,在中度可能性患者中为 30%,在高度可能性患者中为 65%。[93]Ceriani E, Combescure C, Le Gal G, et al. Clinical prediction rules for pulmonary embolism: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Thromb Haemost. 2010 May;8(5):957-70.https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/j.1538-7836.2010.03801.xhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20149072?tool=bestpractice.com
很有可能发生 PE(高临床可能性)
对于临床(验前)概率为很有可能发生 PE 的患者,应为其预约多层螺旋 CTPA 检测。[74]Raja AS, Greenberg JO, Qaseem A, et al. Evaluation of patients with suspected acute pulmonary embolism: best practice advice from the Clinical Guidelines Committee of the American College of Physicians. Ann Intern Med. 2015 Nov 3;163(9):701-11.http://annals.org/aim/fullarticle/2443959/evaluation-patients-suspected-acute-pulmonary-embolism-best-practice-advice-fromhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26414967?tool=bestpractice.com[75]Konstantinides SV, Torbicki A, Agnelli G, et al; Task Force for the Diagnosis and Management of Acute Pulmonary Embolism of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). 2014 ESC guidelines on the diagnosis and management of acute pulmonary embolism. Eur Heart J. 2014 Nov 14;35(43):3033-69.https://academic.oup.com/eurheartj/article/35/43/3033/503581http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25173341?tool=bestpractice.com肺通气/灌注扫描可有效排除 PE,并且为一种无辐射和无需造影剂的操作。[75]Konstantinides SV, Torbicki A, Agnelli G, et al; Task Force for the Diagnosis and Management of Acute Pulmonary Embolism of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). 2014 ESC guidelines on the diagnosis and management of acute pulmonary embolism. Eur Heart J. 2014 Nov 14;35(43):3033-69.https://academic.oup.com/eurheartj/article/35/43/3033/503581http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25173341?tool=bestpractice.com 不应进行 D-二聚体检测:血浆 D-二聚体水平正常并不能排除这类患者影像学检查的需要。[74]Raja AS, Greenberg JO, Qaseem A, et al. Evaluation of patients with suspected acute pulmonary embolism: best practice advice from the Clinical Guidelines Committee of the American College of Physicians. Ann Intern Med. 2015 Nov 3;163(9):701-11.http://annals.org/aim/fullarticle/2443959/evaluation-patients-suspected-acute-pulmonary-embolism-best-practice-advice-fromhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26414967?tool=bestpractice.com
不太可能发生 PE(中度或低临床可能性)
欧洲指南推荐,对于存在中度或低 PE 临床可能性的患者来说,应先进行 D-二聚体检测以决定是否需要影像学检查。[75]Konstantinides SV, Torbicki A, Agnelli G, et al; Task Force for the Diagnosis and Management of Acute Pulmonary Embolism of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). 2014 ESC guidelines on the diagnosis and management of acute pulmonary embolism. Eur Heart J. 2014 Nov 14;35(43):3033-69.https://academic.oup.com/eurheartj/article/35/43/3033/503581http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25173341?tool=bestpractice.com
美国内科医师学会的指南推荐,对于 PE 的临床可能性非常低的患者,应使用 PERC。[74]Raja AS, Greenberg JO, Qaseem A, et al. Evaluation of patients with suspected acute pulmonary embolism: best practice advice from the Clinical Guidelines Committee of the American College of Physicians. Ann Intern Med. 2015 Nov 3;163(9):701-11.http://annals.org/aim/fullarticle/2443959/evaluation-patients-suspected-acute-pulmonary-embolism-best-practice-advice-fromhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26414967?tool=bestpractice.com
认为在符合所有标准(年龄 <50 岁;初始心率<100 bpm;室内空气中初始氧饱和度 >94%;无单侧腿肿;无咯血;在最近 4 周内无手术或外伤;无静脉血栓栓塞 [VTE] 史;未使用雌激素)的患者中, PE 的风险低于检测的风险,因此不需要行进一步检查。可使用 D-二聚体检测对不符合所有 PERC 标准的患者进行分类。[74]Raja AS, Greenberg JO, Qaseem A, et al. Evaluation of patients with suspected acute pulmonary embolism: best practice advice from the Clinical Guidelines Committee of the American College of Physicians. Ann Intern Med. 2015 Nov 3;163(9):701-11.http://annals.org/aim/fullarticle/2443959/evaluation-patients-suspected-acute-pulmonary-embolism-best-practice-advice-fromhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26414967?tool=bestpractice.com
一项关于评估使用 PERC 排除 PE 的 Meta 分析报道的敏感度为 97%。[94]Singh B, Mommer SK, Erwin PJ, et al. Pulmonary embolism rule-out criteria (PERC) in pulmonary embolism - revisited: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Emerg Med J. 2013 Sep;30(9):701-6.http://emj.bmj.com/content/30/9/701.longhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23038695?tool=bestpractice.com
D-二聚体检测
以下情况应进行 D-二聚体检测:
有中度 PE 临床可能性的血流动力学稳定患者[74]Raja AS, Greenberg JO, Qaseem A, et al. Evaluation of patients with suspected acute pulmonary embolism: best practice advice from the Clinical Guidelines Committee of the American College of Physicians. Ann Intern Med. 2015 Nov 3;163(9):701-11.http://annals.org/aim/fullarticle/2443959/evaluation-patients-suspected-acute-pulmonary-embolism-best-practice-advice-fromhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26414967?tool=bestpractice.com
初始风险分层认为患者 PE 风险很低且不满足所有 PERC 标准的患者[74]Raja AS, Greenberg JO, Qaseem A, et al. Evaluation of patients with suspected acute pulmonary embolism: best practice advice from the Clinical Guidelines Committee of the American College of Physicians. Ann Intern Med. 2015 Nov 3;163(9):701-11.http://annals.org/aim/fullarticle/2443959/evaluation-patients-suspected-acute-pulmonary-embolism-best-practice-advice-fromhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26414967?tool=bestpractice.com
初始风险分层认为患者 PE 风险很低且未接受 PERC 评估的患者。
临床医生不应对 PE 临床可能性很高的患者进行 D-二聚体测量。[74]Raja AS, Greenberg JO, Qaseem A, et al. Evaluation of patients with suspected acute pulmonary embolism: best practice advice from the Clinical Guidelines Committee of the American College of Physicians. Ann Intern Med. 2015 Nov 3;163(9):701-11.http://annals.org/aim/fullarticle/2443959/evaluation-patients-suspected-acute-pulmonary-embolism-best-practice-advice-fromhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26414967?tool=bestpractice.com
对于验前概率提示不太可能发生(中度或低临床可能性)PE 的患者,D-二聚体检测的敏感度非常高 (>95%)。[74]Raja AS, Greenberg JO, Qaseem A, et al. Evaluation of patients with suspected acute pulmonary embolism: best practice advice from the Clinical Guidelines Committee of the American College of Physicians. Ann Intern Med. 2015 Nov 3;163(9):701-11.http://annals.org/aim/fullarticle/2443959/evaluation-patients-suspected-acute-pulmonary-embolism-best-practice-advice-fromhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26414967?tool=bestpractice.com[95]Crawford F, Andras A, Welch K, et al. D-dimer test for excluding the diagnosis of pulmonary embolism. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Aug 5;(8):CD010864.http://cochranelibrary-wiley.com/doi/10.1002/14651858.CD010864.pub2/fullhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27494075?tool=bestpractice.com但其特异性较低且可能随患者年龄增加而有所下降。[74]Raja AS, Greenberg JO, Qaseem A, et al. Evaluation of patients with suspected acute pulmonary embolism: best practice advice from the Clinical Guidelines Committee of the American College of Physicians. Ann Intern Med. 2015 Nov 3;163(9):701-11.http://annals.org/aim/fullarticle/2443959/evaluation-patients-suspected-acute-pulmonary-embolism-best-practice-advice-fromhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26414967?tool=bestpractice.com[95]Crawford F, Andras A, Welch K, et al. D-dimer test for excluding the diagnosis of pulmonary embolism. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Aug 5;(8):CD010864.http://cochranelibrary-wiley.com/doi/10.1002/14651858.CD010864.pub2/fullhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27494075?tool=bestpractice.com一项 Meta 分析的结果显示,在年龄 >50 岁的患者中使用经年龄校正的 D-二聚体阈值,在增加 PE 特异性的同时可维持敏感度。[96]Schouten HJ, Geersing GJ, Koek HL, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of conventional or age adjusted D-dimer cut-off values in older patients with suspected venous thromboembolism: systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ. 2013 May 3;346:f2492.https://www.bmj.com/content/346/bmj.f2492.longhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23645857?tool=bestpractice.com对于癌症患者,使用经年龄校正的 D-二聚体阈值可将不经影像学检查、而通过临床决策规则和 D-二聚体来排除 PE 患者的比例翻倍。[97]Wilts IT, Le Gal G, Den Exter PL, et al. Performance of the age-adjusted cut-off for D-dimer in patients with cancer and suspected pulmonary embolism. Thromb Res. 2017 Apr;152:49-51.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28226257?tool=bestpractice.com
血 D-二聚体水平正常(理想情况下经年龄校正 [年龄 x 10 ng/mL,50 岁以上],或 <500 ng/mL)可安全地排除验前概率为不太可能发生(中度或低概率)PE 的患者发生 PE 的可能性,且无需进一步检测。[74]Raja AS, Greenberg JO, Qaseem A, et al. Evaluation of patients with suspected acute pulmonary embolism: best practice advice from the Clinical Guidelines Committee of the American College of Physicians. Ann Intern Med. 2015 Nov 3;163(9):701-11.http://annals.org/aim/fullarticle/2443959/evaluation-patients-suspected-acute-pulmonary-embolism-best-practice-advice-fromhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26414967?tool=bestpractice.com[85]Konstantinides SV, Barco S, Lankeit M, et al. Management of pulmonary embolism: an update. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2016 Mar 1;67(8):976-90.http://www.onlinejacc.org/content/67/8/976http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26916489?tool=bestpractice.com这些患者 3 个月内发生 PE 的风险 <1%。[98]Carrier M, Righini M, Djurabi RK, et al. VIDAS D-dimer in combination with clinical pre-test probability to rule out pulmonary embolism: a systematic review of management outcome studies. Thromb Haemost. 2009 May;101(5):886-92.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19404542?tool=bestpractice.com[99]Agnelli G, Becattini C. Acute pulmonary embolism. N Engl J Med. 2010 Jul 15;363(3):266-74.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20592294?tool=bestpractice.com
D-二聚体水平不正常的患者应接受多层螺旋 CTPA 检测(或者若禁忌行 CTPA,可进行肺通气/灌注扫描检测)以确诊或排除 PE 诊断。[74]Raja AS, Greenberg JO, Qaseem A, et al. Evaluation of patients with suspected acute pulmonary embolism: best practice advice from the Clinical Guidelines Committee of the American College of Physicians. Ann Intern Med. 2015 Nov 3;163(9):701-11.http://annals.org/aim/fullarticle/2443959/evaluation-patients-suspected-acute-pulmonary-embolism-best-practice-advice-fromhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26414967?tool=bestpractice.com[75]Konstantinides SV, Torbicki A, Agnelli G, et al; Task Force for the Diagnosis and Management of Acute Pulmonary Embolism of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). 2014 ESC guidelines on the diagnosis and management of acute pulmonary embolism. Eur Heart J. 2014 Nov 14;35(43):3033-69.https://academic.oup.com/eurheartj/article/35/43/3033/503581http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25173341?tool=bestpractice.com[85]Konstantinides SV, Barco S, Lankeit M, et al. Management of pulmonary embolism: an update. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2016 Mar 1;67(8):976-90.http://www.onlinejacc.org/content/67/8/976http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26916489?tool=bestpractice.com
初始影像学检查
CTPA 可通过直接观察到肺动脉内血栓而进行确诊,其可表现为部分或全部管腔内充盈缺损。对于肺段或亚肺段充盈缺损的 PE,确诊 PE 的似然比为 24.1(范围是 12.4-46.7),而排除 PE 的似然比为 0.11(范围是 0.06-0.19),这意味着 CTPA 在所有先进的非侵入性影像检查方法中,有着最高的诊断准确性。[100]Perrier A, Roy PM, Sanchez O, et al. Multidetector-row computed tomography in suspected pulmonary embolism. N Engl J Med. 2005 Apr 28;352(17):1760-8.https://www.nejm.org/doi/10.1056/NEJMoa042905http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15858185?tool=bestpractice.com [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 增强 CTPA 扫描可显示右肺动脉亚段栓子(箭头所指部位)由 Seth W. Clemens 收集;经许可后使用 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 增强 CTPA 扫描可显示右肺动脉亚段栓子(箭头所指部位)由 Seth W. Clemens 收集;经许可后使用 [Citation ends].
肺通气/灌注扫描(首选使用单光子发射型计算机断层显像 [SPECT],可能减少扫描结果不确定的次数),是 CTPA 的替代检查。[101]Phillips JJ, Straiton J, Staff RT. Planar and SPECT ventilation/perfusion imaging and computed tomography for the diagnosis of pulmonary embolism: a systematic review and meta-analysis of the literature, and cost and dose comparison. Eur J Radiol. 2015 Jul;84(7):1392-400.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25868674?tool=bestpractice.com肺通气-灌注扫描结果阴性可有效排除肺栓塞。肺通气/灌注扫描是一种无辐射和无需造影剂的操作,且可能适用于有 CT 禁忌证和相对禁忌证的患者(例如,造影剂过敏、轻度至中度肾衰竭、妊娠、年轻患者)。[75]Konstantinides SV, Torbicki A, Agnelli G, et al; Task Force for the Diagnosis and Management of Acute Pulmonary Embolism of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). 2014 ESC guidelines on the diagnosis and management of acute pulmonary embolism. Eur Heart J. 2014 Nov 14;35(43):3033-69.https://academic.oup.com/eurheartj/article/35/43/3033/503581http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25173341?tool=bestpractice.com
其他影像学检查
胸部 X 线检查正常并不能排除 PE 的诊断,且检查发现可能仅提示有 PE。[102]Kirsch J, Brown RK, Henry TS, et al; Expert Panels on Cardiac and Thoracic Imaging, American College of Radiology. ACR appropriateness criteria®: acute chest pain - suspected pulmonary embolism. J Am Coll Radiol. 2017 May;14(5S):S2-12.https://www.jacr.org/article/S1546-1440(17)30207-7/fulltexthttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28473076?tool=bestpractice.com
心电图 (ECG) 并不能绝对确立或排除 PE 的诊断,且特定的检查发现可能仅提示有 PE。[77]Bajaj N, Bozarth AL, Guillot J, et al. Clinical features in patients with pulmonary embolism at a community hospital: analysis of 4 years of data. J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2014 Apr;37(3):287-92.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23681675?tool=bestpractice.com[103]Brown G, Hogg K. Best evidence topic report: diagnostic utility of electrocardiogram for diagnosing pulmonary embolism. Emerg Med J. 2005 Oct;22(10):729-30.http://emj.bmj.com/content/22/10/729.2.longhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16189038?tool=bestpractice.com[104]Sukhija R, Aronow WS, Ahn C, et al. Electrocardiographic abnormalities in patients with right ventricular dilation due to acute pulmonary embolism. Cardiology. 2006;105(1):57-60.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16254425?tool=bestpractice.com但是,心电图可用来评估不伴休克或低血压的 PE 确诊患者的右心室功能。[75]Konstantinides SV, Torbicki A, Agnelli G, et al; Task Force for the Diagnosis and Management of Acute Pulmonary Embolism of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). 2014 ESC guidelines on the diagnosis and management of acute pulmonary embolism. Eur Heart J. 2014 Nov 14;35(43):3033-69.https://academic.oup.com/eurheartj/article/35/43/3033/503581http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25173341?tool=bestpractice.com[105]Kearon C, Akl EA, Ornelas J, et al; American College of Chest Physicians. Antithrombotic therapy for VTE disease: CHEST guideline and expert panel report. Chest. 2016 Feb;149(2):315-52.https://journal.chestnet.org/article/S0012-3692(15)00335-9/fulltexthttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26867832?tool=bestpractice.com右心室功能不全可预示结局不良且可通过此对这些患者进行风险分层。[106]Vanni S, Polidori G, Vergara R, et al. Prognostic value of ECG among patients with acute pulmonary embolism and normal blood pressure. Am J Med. 2009 Mar;122(3):257-64.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19272487?tool=bestpractice.com[107]Jaff MR, McMurtry MS, Archer SL, et al. Management of massive and submassive pulmonary embolism, iliofemoral deep vein thrombosis, and chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2011 Apr 26;123(16):1788-830.http://circ.ahajournals.org/content/123/16/1788.longhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21422387?tool=bestpractice.com[108]Weekes AJ, Thacker G, Troha D, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of right ventricular dysfunction markers in normotensive emergency department patients with acute pulmonary embolism. Ann Emerg Med. 2016 Sep;68(3):277-91.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26973178?tool=bestpractice.com若无法使用确诊性影像学检测方法,对于表现为休克或低血压的疑似 PE 患者可考虑进行心电图检查。[75]Konstantinides SV, Torbicki A, Agnelli G, et al; Task Force for the Diagnosis and Management of Acute Pulmonary Embolism of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). 2014 ESC guidelines on the diagnosis and management of acute pulmonary embolism. Eur Heart J. 2014 Nov 14;35(43):3033-69.https://academic.oup.com/eurheartj/article/35/43/3033/503581http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25173341?tool=bestpractice.com[85]Konstantinides SV, Barco S, Lankeit M, et al. Management of pulmonary embolism: an update. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2016 Mar 1;67(8):976-90.http://www.onlinejacc.org/content/67/8/976http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26916489?tool=bestpractice.com
可使用磁共振血管成像和磁共振灌注成像来评估中央和各节段动脉。[102]Kirsch J, Brown RK, Henry TS, et al; Expert Panels on Cardiac and Thoracic Imaging, American College of Radiology. ACR appropriateness criteria®: acute chest pain - suspected pulmonary embolism. J Am Coll Radiol. 2017 May;14(5S):S2-12.https://www.jacr.org/article/S1546-1440(17)30207-7/fulltexthttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28473076?tool=bestpractice.com诊断急性 PE 时,通常不使用经胸超声心动图(虽然该检查可能有助于发现右心室劳损,并辅助预后)。[102]Kirsch J, Brown RK, Henry TS, et al; Expert Panels on Cardiac and Thoracic Imaging, American College of Radiology. ACR appropriateness criteria®: acute chest pain - suspected pulmonary embolism. J Am Coll Radiol. 2017 May;14(5S):S2-12.https://www.jacr.org/article/S1546-1440(17)30207-7/fulltexthttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28473076?tool=bestpractice.com对于确诊急性 PE 的患者,超声心动图发现右心血栓的证据与上升的 30 天死亡率呈显著相关。[109]Barrios D, Rosa-Salazar V, Morillo R, et al. Prognostic significance of right heart thrombi in patients with acute symptomatic pulmonary embolism: systematic review and meta-analysis. Chest. 2017 Feb;151(2):409-16.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27746202?tool=bestpractice.com [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Gd-MRA 显示右肺动脉栓塞(箭头所指部位)由 Seth W. Clemens 收集;经许可后使用 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Gd-MRA 显示右肺动脉栓塞(箭头所指部位)由 Seth W. Clemens 收集;经许可后使用 [Citation ends].
尽管诊断准确,肺动脉造影很少用于确诊或排除 PE。[75]Konstantinides SV, Torbicki A, Agnelli G, et al; Task Force for the Diagnosis and Management of Acute Pulmonary Embolism of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). 2014 ESC guidelines on the diagnosis and management of acute pulmonary embolism. Eur Heart J. 2014 Nov 14;35(43):3033-69.https://academic.oup.com/eurheartj/article/35/43/3033/503581http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25173341?tool=bestpractice.com[110]Kearon C. Diagnosis of suspected venous thromboembolism. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2016 Dec 2;2016(1):397-403.http://asheducationbook.hematologylibrary.org/content/2016/1/397.longhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27913507?tool=bestpractice.com肺动脉造影存在致病/死亡风险,且(创伤性更小的)CTPA 可提供与此相当的诊断精度。[75]Konstantinides SV, Torbicki A, Agnelli G, et al; Task Force for the Diagnosis and Management of Acute Pulmonary Embolism of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). 2014 ESC guidelines on the diagnosis and management of acute pulmonary embolism. Eur Heart J. 2014 Nov 14;35(43):3033-69.https://academic.oup.com/eurheartj/article/35/43/3033/503581http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25173341?tool=bestpractice.com[111]Stein PD, Athanasoulis C, Alavi A, et al. Complications and validity of pulmonary angiography in acute pulmonary embolism. Circulation. 1992 Feb;85(2):462-8.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/1735144?tool=bestpractice.com
实验室检查
基础实验室检查,包括凝血酶原时间 (PT)、活化部分凝血活酶时间 (aPTT)、和国际标准化比值 (INR) 对于辅助做出关于安全性和初始抗凝剂种类选择的决定非常重要。全血细胞计数可能检测到血液学的异常。
不需对所有偶发静脉血栓栓塞事件的患者行血栓形成倾向筛查;然而,如果其血栓形成部位较为特殊、有较大栓子负荷或有复发性栓塞事件发生,则此筛查可能具有帮助。若提示进行易栓症筛查,则应推迟至抗凝治疗完成后至少 3 个月,因有些易栓症检测可能会受急性血栓形成或抗凝治疗的影响。[112]Stevens SM, Woller SC, Bauer KA, et al. Guidance for the evaluation and treatment of hereditary and acquired thrombophilia. J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2016 Jan;41(1):154-64.https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11239-015-1316-1http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26780744?tool=bestpractice.com或者可采取两步筛查方法,先进行能够在初期抗凝过程中取得可靠结果的易栓症测试(即,凝血因子 Ⅴ Leiden 突变、凝血素 G20210A 突变、心磷脂、及抗 β2-糖蛋白 I 抗体),若结果正常,则可停止抗凝治疗。接下来进行其余的检测,这些指标的血清水平可能在血栓形成的超急性期或由于使用抗凝剂(例如,狼疮抗凝物、蛋白 C、蛋白 S、抗凝血酶)而有所下降。[112]Stevens SM, Woller SC, Bauer KA, et al. Guidance for the evaluation and treatment of hereditary and acquired thrombophilia. J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2016 Jan;41(1):154-64.https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11239-015-1316-1http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26780744?tool=bestpractice.com
低氧血症被认为是急性 PE 的一项典型的检查发现,但动脉血气分析无论是单独使用还是与其他临床变量联合应用,在疑似 PE 中的诊断作用都很有限。[75]Konstantinides SV, Torbicki A, Agnelli G, et al; Task Force for the Diagnosis and Management of Acute Pulmonary Embolism of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). 2014 ESC guidelines on the diagnosis and management of acute pulmonary embolism. Eur Heart J. 2014 Nov 14;35(43):3033-69.https://academic.oup.com/eurheartj/article/35/43/3033/503581http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25173341?tool=bestpractice.com[113]Rodger MA, Carrier M, Jones GN, et al. Diagnostic value of arterial blood gas measurement in suspected pulmonary embolism. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2000 Dec;162(6):2105-8.https://www.atsjournals.org/doi/full/10.1164/ajrccm.162.6.2004204http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11112122?tool=bestpractice.comPaO₂ <80 mmHg、PaCO₂ <36 mmHg、或肺泡-动脉氧分压差 (A–aO₂) 异常,均不能预测疑似 PE 的患者患有 PE。[113]Rodger MA, Carrier M, Jones GN, et al. Diagnostic value of arterial blood gas measurement in suspected pulmonary embolism. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2000 Dec;162(6):2105-8.https://www.atsjournals.org/doi/full/10.1164/ajrccm.162.6.2004204http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11112122?tool=bestpractice.com对于动脉血气 (ABG) 结果正常的疑似急性 PE 患者,在没有心肺疾病的患者中和已患有心肺疾病的患者中,分别有 38% 和 14% 的患者无法排除 PE 的诊断。[114]Stein PD, Goldhaber SZ, Henry JW, et al. Arterial blood gas analysis in the assessment of suspected acute pulmonary embolism. Chest. 1996 Jan;109(1):78-81.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8549223?tool=bestpractice.com
特殊患者群体
妊娠女性
非妊娠患者 VTE 的症状和体征可能比妊娠女性更具特异性。[85]Konstantinides SV, Barco S, Lankeit M, et al. Management of pulmonary embolism: an update. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2016 Mar 1;67(8):976-90.http://www.onlinejacc.org/content/67/8/976http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26916489?tool=bestpractice.com 美国胸科学会共识指南建议,D-二聚体检测不应该用于排除妊娠时的 PE。[115]Leung AN, Bull TM, Jaeschke R, et al. An official American Thoracic Society/Society of Thoracic Radiology clinical practice guideline: evaluation of suspected pulmonary embolism in pregnancy. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2011 Nov 15;184(10):1200-8.https://www.atsjournals.org/doi/full/10.1164/rccm.201108-1575ST#.UnJdTVNZit8http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22086989?tool=bestpractice.com一项队列研究评估了包括 D-二聚体在内的多个生物标志物对疑似 VTE 的诊断效力,该研究并未发现任何包含有助于诊断或排除 VTE 阈值的候选生物标志物。[116]Hunt BJ, Parmar K, Horspool K, et al. The DiPEP (Diagnosis of PE in Pregnancy) biomarker study: An observational cohort study augmented with additional cases to determine the diagnostic utility of biomarkers for suspected venous thromboembolism during pregnancy and puerperium. Br J Haematol. 2018 Mar;180(5):694-704.https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/bjh.15102http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29359796?tool=bestpractice.com妊娠期间 D-二聚体水平的升高可能通过采用合适的阈值来帮助增加特异性,但还需进一步评估。[85]Konstantinides SV, Barco S, Lankeit M, et al. Management of pulmonary embolism: an update. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2016 Mar 1;67(8):976-90.http://www.onlinejacc.org/content/67/8/976http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26916489?tool=bestpractice.com[117]Chan WS, Lee A, Spencer FA, et al. D-dimer testing in pregnant patients: towards determining the next 'level' in the diagnosis of deep vein thrombosis. J Thromb Haemost. 2010 May;8(5):1004-11.https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/j.1538-7836.2010.03783.xhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20128870?tool=bestpractice.com
应尽量减少有辐射暴露的影像学检查。推荐疑似 PE 的妊娠患者进行双侧静脉压缩超声以确认存在提示 PE 的血栓。[115]Leung AN, Bull TM, Jaeschke R, et al. An official American Thoracic Society/Society of Thoracic Radiology clinical practice guideline: evaluation of suspected pulmonary embolism in pregnancy. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2011 Nov 15;184(10):1200-8.https://www.atsjournals.org/doi/full/10.1164/rccm.201108-1575ST#.UnJdTVNZit8http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22086989?tool=bestpractice.com若疑似 PE,则胸部 X 线检查是首先进行的有辐射的检查。[115]Leung AN, Bull TM, Jaeschke R, et al. An official American Thoracic Society/Society of Thoracic Radiology clinical practice guideline: evaluation of suspected pulmonary embolism in pregnancy. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2011 Nov 15;184(10):1200-8.https://www.atsjournals.org/doi/full/10.1164/rccm.201108-1575ST#.UnJdTVNZit8http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22086989?tool=bestpractice.com对于下一步应进行肺闪烁成像(伴肺通气/灌注扫描)还是 CTPA 仍存在争议。[101]Phillips JJ, Straiton J, Staff RT. Planar and SPECT ventilation/perfusion imaging and computed tomography for the diagnosis of pulmonary embolism: a systematic review and meta-analysis of the literature, and cost and dose comparison. Eur J Radiol. 2015 Jul;84(7):1392-400.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25868674?tool=bestpractice.com 若胸部 X 线检查正常,美国胸科学会共识指南推荐进行肺闪烁成像(伴肺通气/灌注扫描)。[115]Leung AN, Bull TM, Jaeschke R, et al. An official American Thoracic Society/Society of Thoracic Radiology clinical practice guideline: evaluation of suspected pulmonary embolism in pregnancy. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2011 Nov 15;184(10):1200-8.https://www.atsjournals.org/doi/full/10.1164/rccm.201108-1575ST#.UnJdTVNZit8http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22086989?tool=bestpractice.com若妊娠女性的肺通气/灌注扫描结果为非诊断性,且认为其进一步检查是适当的,则可进行 CTPA 检查。[115]Leung AN, Bull TM, Jaeschke R, et al. An official American Thoracic Society/Society of Thoracic Radiology clinical practice guideline: evaluation of suspected pulmonary embolism in pregnancy. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2011 Nov 15;184(10):1200-8.https://www.atsjournals.org/doi/full/10.1164/rccm.201108-1575ST#.UnJdTVNZit8http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22086989?tool=bestpractice.com若妊娠女性需进行肺部扫描,使用的放射性药物剂量应减少至原来的一半;应延长采集时间,以达到充分的成像。[101]Phillips JJ, Straiton J, Staff RT. Planar and SPECT ventilation/perfusion imaging and computed tomography for the diagnosis of pulmonary embolism: a systematic review and meta-analysis of the literature, and cost and dose comparison. Eur J Radiol. 2015 Jul;84(7):1392-400.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25868674?tool=bestpractice.com
青少年及青年
应谨慎使用 CTPA,特别是当可通过其他辐射暴露更少的、非侵入性的方式排除 PE 时。[118]Arnold RW, Janitz E, Poulton TB, et al. Pulmonary CT angiography to evaluate for pulmonary embolism in children visiting adult-centered community hospitals. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2011 Jun;196(6):W823-30.https://www.ajronline.org/doi/full/10.2214/AJR.10.5951http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21606276?tool=bestpractice.com
PE 严重程度指数较低
CTPA 似乎可增加诊断为亚肺段 PE 的患者比例,但并未降低 3 个月内的血栓栓塞风险,这提示亚肺段 PE 可能无临床意义。[119]Carrier M, Righini M, Wells PS, et al. Subsegmental pulmonary embolism diagnosed by computed tomography: incidence and clinical implications. A systematic review and meta-analysis of the management outcome studies. J Thromb Haemost. 2010 Aug;8(8):1716-22.https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/j.1538-7836.2010.03938.xhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20546118?tool=bestpractice.com 对于有亚肺段 PE(即,没有累及更近端的肺动脉)且双腿没有近端 DVT 的患者、以及 VTE 复发风险较低的患者,推荐进行临床监测,而非抗凝治疗。[105]Kearon C, Akl EA, Ornelas J, et al; American College of Chest Physicians. Antithrombotic therapy for VTE disease: CHEST guideline and expert panel report. Chest. 2016 Feb;149(2):315-52.https://journal.chestnet.org/article/S0012-3692(15)00335-9/fulltexthttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26867832?tool=bestpractice.com
 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 原始和简化 Wells 评分标准(修订)由 BMJ Knowledge Centre 编制 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 原始和简化 Wells 评分标准(修订)由 BMJ Knowledge Centre 编制 [Citation ends]. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 原始和简化 Geneva 评分标准(改良)由 BMJ Knowledge Centre 编制 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 原始和简化 Geneva 评分标准(改良)由 BMJ Knowledge Centre 编制 [Citation ends]. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 增强 CTPA 扫描可显示右肺动脉亚段栓子(箭头所指部位)由 Seth W. Clemens 收集;经许可后使用 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 增强 CTPA 扫描可显示右肺动脉亚段栓子(箭头所指部位)由 Seth W. Clemens 收集;经许可后使用 [Citation ends]. [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Gd-MRA 显示右肺动脉栓塞(箭头所指部位)由 Seth W. Clemens 收集;经许可后使用 [Citation ends].
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: Gd-MRA 显示右肺动脉栓塞(箭头所指部位)由 Seth W. Clemens 收集;经许可后使用 [Citation ends]. 