药物治疗
初始治疗从长疗程的抗生素开始。特别小组推荐12周的疗程。[20]Slavin RG, Spector SL, Bernstein IL, et al. The diagnosis and management of sinusitis: a practice parameter update. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2005;116(suppl 6):S13-S47.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16416688?tool=bestpractice.com但无强有力证据,且在临床实践中不常用。一篇系统评价推荐短疗程(<3 周)抗生素治疗作为治疗选择,这些抗生素不包括大环内酯类,因为有证据表明只有长疗程大环内酯类抗生素对特定患者才有效。[26]Soler ZM, Oyer SL, Kern RC, et al. Antimicrobials and chronic rhinosinusitis with or without polyposis in adults: an evidenced-based review with recommendations. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2013;3:31-47.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22736403?tool=bestpractice.com根据美国鼻科学会的社会调查,大多数鼻科学家使用的最短治疗疗程为3-4周。虽然更受欢迎的治疗方法为细菌培养指导的抗生素选择,常用治疗方法为广谱抗生素覆盖。
美国食品药品监督管理局 (FDA) 已发布了关于氟喹诺酮使用的安全性警告,称对于有其他治疗选择的鼻窦炎、支气管炎和无并发症尿路感染患者,与此类抗生素相关的严重副作用超过其获益。[27]US Food and Drug Administration. Fluoroquinolone antibacterial drugs: drug safety communication - FDA advises restricting use for certain uncomplicated infections. May 2016. http://www.fda.gov (last accessed 27 September 2017).https://www.fda.gov/downloads/Drugs/DrugSafety/UCM500591.pdfFDA 建议,对于上述患者,仅应在无其他替代选择情况下考虑使用氟喹诺酮类药物。
专家建议在使用抗生素的同时,使用局部鼻内给药皮质类固醇。[19]Rosenfeld RM, Piccirillo JF, Chandrasekhar SS, et al. Clinical practice guideline (update): adult sinusitis. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2015;152(suppl 2):S1-S39.http://oto.sagepub.com/content/152/2_suppl/S1.longhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25832968?tool=bestpractice.com[28]Mösges R, Heubach CP. What is the evidence for non-antibiotic drug therapy of rhinosinusitis? Laryngorhinootologie. 2011;90:740-746.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22016266?tool=bestpractice.com[29]Chong LY, Head K, Hopkins C, et al. Intranasal steroids versus placebo or no intervention for chronic rhinosinusitis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016;(4):CD011996.http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/14651858.CD011996.pub2/fullhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27115217?tool=bestpractice.com[30]Chong LY, Head K, Hopkins C, et al. Different types of intranasal steroids for chronic rhinosinusitis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016;(4):CD011993.http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/14651858.CD011993.pub2/fullhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27115215?tool=bestpractice.com[31]Wang C, Lou H, Wang X, et al. Effect of budesonide transnasal nebulization in patients with eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2015;135:922-929.http://www.jacionline.org/article/S0091-6749(14)01513-9/fulltexthttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25483598?tool=bestpractice.com[32]Rudmik L, Soler ZM. Medical therapies for adult chronic sinusitis: a systematic review. JAMA. 2015;314:926-939.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26325561?tool=bestpractice.com鼻腔生理盐水冲洗也应该贯穿治疗的全程。[32]Rudmik L, Soler ZM. Medical therapies for adult chronic sinusitis: a systematic review. JAMA. 2015;314:926-939.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26325561?tool=bestpractice.com[33]Chong LY, Head K, Hopkins C, et al. Saline irrigation for chronic rhinosinusitis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016;(4):CD011995.http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/14651858.CD011995.pub2/fullhttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27115216?tool=bestpractice.com
可在所有患者中考虑辅助治疗,包括短疗程服用口服皮质类固醇、减充血剂,甚至白三烯受体拮抗剂(尤其在有哮喘、息肉或严重的过敏性鼻炎的情况下)。[20]Slavin RG, Spector SL, Bernstein IL, et al. The diagnosis and management of sinusitis: a practice parameter update. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2005;116(suppl 6):S13-S47.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16416688?tool=bestpractice.com[28]Mösges R, Heubach CP. What is the evidence for non-antibiotic drug therapy of rhinosinusitis? Laryngorhinootologie. 2011;90:740-746.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22016266?tool=bestpractice.com[32]Rudmik L, Soler ZM. Medical therapies for adult chronic sinusitis: a systematic review. JAMA. 2015;314:926-939.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26325561?tool=bestpractice.com[34]Steinke JW, Borish L. Leukotriene receptors in rhinitis and sinusitis. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2004;4:217-223.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15056404?tool=bestpractice.com 对于伴有鼻息肉或鼻内窥镜下明显水肿的患者,常考虑口服皮质类固醇。[28]Mösges R, Heubach CP. What is the evidence for non-antibiotic drug therapy of rhinosinusitis? Laryngorhinootologie. 2011;90:740-746.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22016266?tool=bestpractice.com[32]Rudmik L, Soler ZM. Medical therapies for adult chronic sinusitis: a systematic review. JAMA. 2015;314:926-939.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26325561?tool=bestpractice.com也可以在术前准备或急性加重期使用。如果患者有过敏性症状,抗组胺药是有效的。对于合适的慢性或复发性鼻窦炎、过敏性鼻炎或手术后鼻窦炎仍存在的患者,可能需要过敏会诊,以开展后续免疫疗法。[20]Slavin RG, Spector SL, Bernstein IL, et al. The diagnosis and management of sinusitis: a practice parameter update. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2005;116(suppl 6):S13-S47.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16416688?tool=bestpractice.com有哮喘的患者需要优化其肺部疾病治疗。戒烟将有助于药物和手术治疗的效果。
手术治疗
治疗后仍症状显著,且CT显示鼻窦有炎症的患者适合于手术治疗。内镜鼻窦手术(ESS)通过使鼻窦开口和通道更宽(例如窦口鼻道复合体)来重建鼻窦通气和引流通道。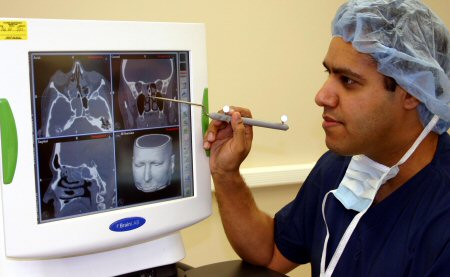 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 在手术导航工作站的术前计划来自Raj Sindwani医生的个人收藏 [Citation ends]. 对于病变范围广,有手术史,或者需要在敏感解剖区域(例如额窦或蝶窦)手术的患者,提倡使用术中导航(或图像引导手术)。[35]Sindwani R, Metson R. Image-guided frontal sinus surgery. Otolaryngol Clin North Am. 2005;38:461-471.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15907895?tool=bestpractice.com[36]Smith TL, Stewart MG, Orlandi RR, et al. Indications for image-guided sinus surgery: the current evidence. Am J Rhinol. 2007;21:80-83.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17283566?tool=bestpractice.com图像引导系统对术前计划和术中定位有益,使得手术过程更安全。
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 在手术导航工作站的术前计划来自Raj Sindwani医生的个人收藏 [Citation ends]. 对于病变范围广,有手术史,或者需要在敏感解剖区域(例如额窦或蝶窦)手术的患者,提倡使用术中导航(或图像引导手术)。[35]Sindwani R, Metson R. Image-guided frontal sinus surgery. Otolaryngol Clin North Am. 2005;38:461-471.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15907895?tool=bestpractice.com[36]Smith TL, Stewart MG, Orlandi RR, et al. Indications for image-guided sinus surgery: the current evidence. Am J Rhinol. 2007;21:80-83.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17283566?tool=bestpractice.com图像引导系统对术前计划和术中定位有益,使得手术过程更安全。 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 图像引导的内镜鼻窦手术使用光学基础的手术导航系统来自Raj Sindwani医生的个人收藏 [Citation ends].这项技术目前已广泛开展,但是仍未列为基本要求或标准治疗。潜在的手术并发症包括出血,感染,脑损伤或脑脊液漏,眼眶损伤(淤青,复视或失明),鼻窦疾病残留或复发,需要再次手术,嗅觉失调,和全麻相关问题。严重并发症(包括损伤颅内和眼眶结构)非常罕见(<1%)。传统的ESS手术耐受性很好,不会引起面部的淤青或伤口。很少使用鼻腔填塞。患者术后症状改善明显,短期恢复即可恢复工作。[37]Mehta U, Huber TC, Sindwani R. Patient expectations and recovery following endoscopic sinus surgery. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2006;134:483-487.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16500449?tool=bestpractice.com当术前给患者咨询时,很重要的一点是要说明,术后鼻塞改善最显著,面部疼痛和流脓涕改善程度为中等,但是头痛和失嗅改善最不明显。[38]Chester AC, Antisdel JL, Sindwani R. Symptom-specific outcomes of endoscopic sinus surgery: a systematic review. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2009;140:633-639.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19393402?tool=bestpractice.com乏力和躯体疼痛在ESS术后也会有所改善。[39]Chester AC, Sindwani R, Smith TL, et al. Systematic review of change in bodily pain after sinus surgery. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2008;139:759-765.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19041499?tool=bestpractice.com[40]Chester AC, Sindwani R, Smith TL, et al. Fatigue improvement following endoscopic sinus surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Laryngoscope. 2008;118:730-739.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18216743?tool=bestpractice.com
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 图像引导的内镜鼻窦手术使用光学基础的手术导航系统来自Raj Sindwani医生的个人收藏 [Citation ends].这项技术目前已广泛开展,但是仍未列为基本要求或标准治疗。潜在的手术并发症包括出血,感染,脑损伤或脑脊液漏,眼眶损伤(淤青,复视或失明),鼻窦疾病残留或复发,需要再次手术,嗅觉失调,和全麻相关问题。严重并发症(包括损伤颅内和眼眶结构)非常罕见(<1%)。传统的ESS手术耐受性很好,不会引起面部的淤青或伤口。很少使用鼻腔填塞。患者术后症状改善明显,短期恢复即可恢复工作。[37]Mehta U, Huber TC, Sindwani R. Patient expectations and recovery following endoscopic sinus surgery. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2006;134:483-487.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16500449?tool=bestpractice.com当术前给患者咨询时,很重要的一点是要说明,术后鼻塞改善最显著,面部疼痛和流脓涕改善程度为中等,但是头痛和失嗅改善最不明显。[38]Chester AC, Antisdel JL, Sindwani R. Symptom-specific outcomes of endoscopic sinus surgery: a systematic review. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2009;140:633-639.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19393402?tool=bestpractice.com乏力和躯体疼痛在ESS术后也会有所改善。[39]Chester AC, Sindwani R, Smith TL, et al. Systematic review of change in bodily pain after sinus surgery. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2008;139:759-765.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19041499?tool=bestpractice.com[40]Chester AC, Sindwani R, Smith TL, et al. Fatigue improvement following endoscopic sinus surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Laryngoscope. 2008;118:730-739.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18216743?tool=bestpractice.com
再次手术可能对于一些患者是必要的。在非鼻息肉患者中,结构问题(例如,在重要区域瘢痕形成,偏曲的中鼻甲堵塞了引流通道)可能导致手术失败,症状复发。在增生性或息肉样变的慢性鼻窦炎患者中,息肉复发(此类患者经常发生)可能需要再次手术。
 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 在手术导航工作站的术前计划来自Raj Sindwani医生的个人收藏 [Citation ends]. 对于病变范围广,有手术史,或者需要在敏感解剖区域(例如额窦或蝶窦)手术的患者,提倡使用术中导航(或图像引导手术)。[35][36]图像引导系统对术前计划和术中定位有益,使得手术过程更安全。
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 在手术导航工作站的术前计划来自Raj Sindwani医生的个人收藏 [Citation ends]. 对于病变范围广,有手术史,或者需要在敏感解剖区域(例如额窦或蝶窦)手术的患者,提倡使用术中导航(或图像引导手术)。[35][36]图像引导系统对术前计划和术中定位有益,使得手术过程更安全。 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 图像引导的内镜鼻窦手术使用光学基础的手术导航系统来自Raj Sindwani医生的个人收藏 [Citation ends].这项技术目前已广泛开展,但是仍未列为基本要求或标准治疗。潜在的手术并发症包括出血,感染,脑损伤或脑脊液漏,眼眶损伤(淤青,复视或失明),鼻窦疾病残留或复发,需要再次手术,嗅觉失调,和全麻相关问题。严重并发症(包括损伤颅内和眼眶结构)非常罕见(<1%)。传统的ESS手术耐受性很好,不会引起面部的淤青或伤口。很少使用鼻腔填塞。患者术后症状改善明显,短期恢复即可恢复工作。[37]当术前给患者咨询时,很重要的一点是要说明,术后鼻塞改善最显著,面部疼痛和流脓涕改善程度为中等,但是头痛和失嗅改善最不明显。[38]乏力和躯体疼痛在ESS术后也会有所改善。[39][40]
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 图像引导的内镜鼻窦手术使用光学基础的手术导航系统来自Raj Sindwani医生的个人收藏 [Citation ends].这项技术目前已广泛开展,但是仍未列为基本要求或标准治疗。潜在的手术并发症包括出血,感染,脑损伤或脑脊液漏,眼眶损伤(淤青,复视或失明),鼻窦疾病残留或复发,需要再次手术,嗅觉失调,和全麻相关问题。严重并发症(包括损伤颅内和眼眶结构)非常罕见(<1%)。传统的ESS手术耐受性很好,不会引起面部的淤青或伤口。很少使用鼻腔填塞。患者术后症状改善明显,短期恢复即可恢复工作。[37]当术前给患者咨询时,很重要的一点是要说明,术后鼻塞改善最显著,面部疼痛和流脓涕改善程度为中等,但是头痛和失嗅改善最不明显。[38]乏力和躯体疼痛在ESS术后也会有所改善。[39][40]