疾病史
肠套叠发病率高峰期为 9 月龄左右,[8]Parashar UD, Holman RC, Cummings KC, et al. Trends in intussusception-associated hospitalizations and deaths among US infants. Pediatrics. 2000;106:1413-1421.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11099597?tool=bestpractice.com多达 75% 的病例于 12 月龄以内发病。[9]O'Ryan M, Lucero Y, Pena A, et al. Two year review of intestinal intussusception in six large hospitals of Santiago, Chile. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2003;22:717-721.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12913773?tool=bestpractice.com[12]Blanch AJ, Perel SB, Acworth JP. Paediatric intussusception: epidemiology and outcome. Emerg Med Australas. 2007;19:45-50.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17305660?tool=bestpractice.com评估时应首先获取完整病史并进行体格检查,重点关注腹痛的性质(绞痛还是持续痛)、是否出现红果酱样便及呕吐。几乎所有肠套叠婴儿都伴有腹痛和呕吐。35%-73% 的病例会出现红果酱样便或直肠出血等典型症状。[5]Justice FA, Auldist AW, Bines JE. Intussusception: trends in clinical presentation and management. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2006;21:842-846.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16704533?tool=bestpractice.com[9]O'Ryan M, Lucero Y, Pena A, et al. Two year review of intestinal intussusception in six large hospitals of Santiago, Chile. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2003;22:717-721.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12913773?tool=bestpractice.com[12]Blanch AJ, Perel SB, Acworth JP. Paediatric intussusception: epidemiology and outcome. Emerg Med Australas. 2007;19:45-50.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17305660?tool=bestpractice.com经常出现进展性嗜睡,且患者可能有近期病毒性疾病史。[5]Justice FA, Auldist AW, Bines JE. Intussusception: trends in clinical presentation and management. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2006;21:842-846.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16704533?tool=bestpractice.com
查体
体格检查应首先评估血液动力学是否稳定。腹部查体时可发现可触及的腹部包块、腹胀,甚至假性腹膜炎。腹部包块可能不易察觉,最好在婴儿处于绞痛间歇期平静时进行检查。临床医生希望在患儿躺在其母亲大腿上时检查包块;这样婴儿不仅可以更加平静,而且当患儿俯卧或侧卧时,包块可能更易触及。
直肠检查可能发现出血,但未发现出血并不能排除诊断。5%-10% 会出现低血容量休克(提示有肠缺血或坏死)。[5]Justice FA, Auldist AW, Bines JE. Intussusception: trends in clinical presentation and management. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2006;21:842-846.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16704533?tool=bestpractice.com
影像学检查
根据腹部平片或CT(较少使用)可发现肠套叠特征性的“靶征”。影像学图片上,肠道横截面显示为靶样。腹部平片最常见的结果是正常,但偶尔可见部分肠梗阻。其他提示性体征包括存在软组织肿块、右下腹空、错位阑尾中有气体及小肠梗阻体征。[11]Sorantin E, Lindbichler F. Management of intussusception. Eur Radiol. 2004;14(suppl 4):L146-L154.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/14752570?tool=bestpractice.com[18]del-Pozo G, Albillos JC, Tejedor D, et al. Intussusception in children: current concepts in diagnosis and enema reduction. Radiographics. 1999;19:299-319.http://pubs.rsna.org/doi/full/10.1148/radiographics.19.2.g99mr14299http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10194781?tool=bestpractice.com如果患有腹膜炎,建议即刻外科会诊,并评估腹部平片是否存在腹腔游离气体。存在腹腔内游离气体则提示肠套叠并发肠穿孔。
可以进行造影剂灌肠(空气或造影剂)以诊断肠套叠,但是存在腹腔内游离气体时,禁忌采用该方法。液体或空气灌肠仍然是传统上最具特异性和敏感性的诊断试验,可明确肠套叠的范围。 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 腹部 X 线显示钡餐通过肠套叠引起的梗阻部位受阻。由 David J. Hackam 医生提供;经许可后使用 [Citation ends].液体造影剂灌肠与空气灌肠的诊断效力可能相当。[18]del-Pozo G, Albillos JC, Tejedor D, et al. Intussusception in children: current concepts in diagnosis and enema reduction. Radiographics. 1999;19:299-319.http://pubs.rsna.org/doi/full/10.1148/radiographics.19.2.g99mr14299http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10194781?tool=bestpractice.com一项 Cochrane 评价指出,在复位肠套叠方面,空气灌肠被认为比液体造影剂更有效,但其证据基础被认为质量较低。[19]Gluckman S, Karpelowsky J, Webster AC, et al. Management for intussusception in children. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017;6:CD006476.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28567798?tool=bestpractice.com
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 腹部 X 线显示钡餐通过肠套叠引起的梗阻部位受阻。由 David J. Hackam 医生提供;经许可后使用 [Citation ends].液体造影剂灌肠与空气灌肠的诊断效力可能相当。[18]del-Pozo G, Albillos JC, Tejedor D, et al. Intussusception in children: current concepts in diagnosis and enema reduction. Radiographics. 1999;19:299-319.http://pubs.rsna.org/doi/full/10.1148/radiographics.19.2.g99mr14299http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10194781?tool=bestpractice.com一项 Cochrane 评价指出,在复位肠套叠方面,空气灌肠被认为比液体造影剂更有效,但其证据基础被认为质量较低。[19]Gluckman S, Karpelowsky J, Webster AC, et al. Management for intussusception in children. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017;6:CD006476.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28567798?tool=bestpractice.com
在许多中心,超声检查是用来诊断肠套叠的优先选择。[20]Navarro O, Dugougeat F, Kornecki A, et al. The impact of imaging in the management of intussusception owing to pathologic lead points in children. A review of 43 cases. Pediatr Radiol. 2000;30:594-603.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11009295?tool=bestpractice.com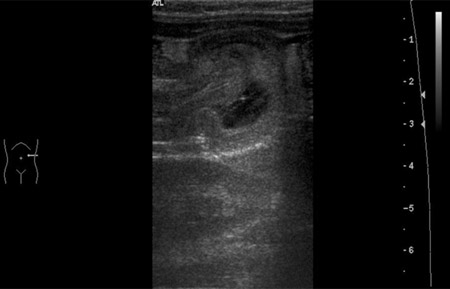 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 超声图像显示一段肠套入邻近肠段中BMJ 病例报告 2009;doi:10.1136/bcr.04.2009.1730;经授权使用 [Citation ends].如果患者临床情况稳定,且未怀疑穿孔,应将超声检查作为肠套叠初始诊断试验。超声检查的诊断准确性达 100%。依据右侧腹壁下存在 3-5 cm 包块,并且存在特征性的圆圈状声像图表现,可诊断为肠套叠。
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 超声图像显示一段肠套入邻近肠段中BMJ 病例报告 2009;doi:10.1136/bcr.04.2009.1730;经授权使用 [Citation ends].如果患者临床情况稳定,且未怀疑穿孔,应将超声检查作为肠套叠初始诊断试验。超声检查的诊断准确性达 100%。依据右侧腹壁下存在 3-5 cm 包块,并且存在特征性的圆圈状声像图表现,可诊断为肠套叠。 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 腹部横向声像图显示圆圈征(肠肿胀环内的同心环)改编自 Student BMJ。2008;16:76.BMJ Publishing Group 版权所有 2010;经授权使用 [Citation ends].超声检查也可以发现是否存在病理性导引点[21]Daneman A, Navarro O. Intussusception. Part 1: a review of diagnostic approaches. Pediatr Radiol. 2003;33:79-85.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12557062?tool=bestpractice.com(一种可导致肠套叠发生的相关肠道解剖学异常 [例如肠息肉或占位性病变])。[2]Hackam DJ, Newman K, Ford HR. Pediatric surgery: gastrointestinal tract. In: Schwartz's principles of surgery, 8th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill; 2005:1493-1494.[3]McCollough M, Sharieff GQ. Abdominal pain in children. Pediatr Clin North Am. 2006;53:107-137.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16487787?tool=bestpractice.com[4]Hackam DJ, Saibil F, Wilson S, et al. Laparoscopic management of intussusception caused by colonic lipomata: a case report and review of the literature. Surg Laparosc Endosc. 1996;6:155-159.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8680642?tool=bestpractice.com
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 腹部横向声像图显示圆圈征(肠肿胀环内的同心环)改编自 Student BMJ。2008;16:76.BMJ Publishing Group 版权所有 2010;经授权使用 [Citation ends].超声检查也可以发现是否存在病理性导引点[21]Daneman A, Navarro O. Intussusception. Part 1: a review of diagnostic approaches. Pediatr Radiol. 2003;33:79-85.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12557062?tool=bestpractice.com(一种可导致肠套叠发生的相关肠道解剖学异常 [例如肠息肉或占位性病变])。[2]Hackam DJ, Newman K, Ford HR. Pediatric surgery: gastrointestinal tract. In: Schwartz's principles of surgery, 8th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill; 2005:1493-1494.[3]McCollough M, Sharieff GQ. Abdominal pain in children. Pediatr Clin North Am. 2006;53:107-137.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16487787?tool=bestpractice.com[4]Hackam DJ, Saibil F, Wilson S, et al. Laparoscopic management of intussusception caused by colonic lipomata: a case report and review of the literature. Surg Laparosc Endosc. 1996;6:155-159.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8680642?tool=bestpractice.com
 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 腹部 X 线显示钡餐通过肠套叠引起的梗阻部位受阻。由 David J. Hackam 医生提供;经许可后使用 [Citation ends].液体造影剂灌肠与空气灌肠的诊断效力可能相当。[18]一项 Cochrane 评价指出,在复位肠套叠方面,空气灌肠被认为比液体造影剂更有效,但其证据基础被认为质量较低。[19]
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 腹部 X 线显示钡餐通过肠套叠引起的梗阻部位受阻。由 David J. Hackam 医生提供;经许可后使用 [Citation ends].液体造影剂灌肠与空气灌肠的诊断效力可能相当。[18]一项 Cochrane 评价指出,在复位肠套叠方面,空气灌肠被认为比液体造影剂更有效,但其证据基础被认为质量较低。[19] [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 超声图像显示一段肠套入邻近肠段中BMJ 病例报告 2009;doi:10.1136/bcr.04.2009.1730;经授权使用 [Citation ends].如果患者临床情况稳定,且未怀疑穿孔,应将超声检查作为肠套叠初始诊断试验。超声检查的诊断准确性达 100%。依据右侧腹壁下存在 3-5 cm 包块,并且存在特征性的圆圈状声像图表现,可诊断为肠套叠。
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 超声图像显示一段肠套入邻近肠段中BMJ 病例报告 2009;doi:10.1136/bcr.04.2009.1730;经授权使用 [Citation ends].如果患者临床情况稳定,且未怀疑穿孔,应将超声检查作为肠套叠初始诊断试验。超声检查的诊断准确性达 100%。依据右侧腹壁下存在 3-5 cm 包块,并且存在特征性的圆圈状声像图表现,可诊断为肠套叠。 [Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 腹部横向声像图显示圆圈征(肠肿胀环内的同心环)改编自 Student BMJ。2008;16:76.BMJ Publishing Group 版权所有 2010;经授权使用 [Citation ends].超声检查也可以发现是否存在病理性导引点[21](一种可导致肠套叠发生的相关肠道解剖学异常 [例如肠息肉或占位性病变])。[2][3][4]
[Figure caption and citation for the preceding image starts]: 腹部横向声像图显示圆圈征(肠肿胀环内的同心环)改编自 Student BMJ。2008;16:76.BMJ Publishing Group 版权所有 2010;经授权使用 [Citation ends].超声检查也可以发现是否存在病理性导引点[21](一种可导致肠套叠发生的相关肠道解剖学异常 [例如肠息肉或占位性病变])。[2][3][4]